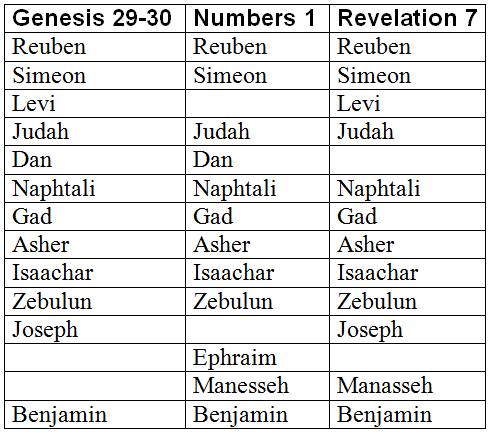
The Israelite tribe of Dan, one of the twelve tribes of Israel, has a unique history filled with both triumph and adversity. Throughout biblical texts, we can trace the journey and fate of this tribe. However, the exact conclusion of this historical account remains a subject of debate among scholars. We will explore the various theories and possibilities surrounding what happened to the Israelite Tribe of Dan.
The tribe of Dan originated from the patriarch Jacob’s sons and occupied a territory along the western coast of Israel. According to the Book of Joshua in the Hebrew Bible, Dan received an inheritance in Canaan, particularly in the northern region. This region included major cities such as Laish and Gaza, which were significant trade and military centers during that era.
Unfortunately, over time, the tribe of Dan faced numerous challenges that would shape its history. One of the most significant events occurred during the period of the Judges, where the tribe struggled to maintain its territory due to external invasions. For example, the Philistines and Amorites waged numerous attacks on Dan’s lands, inevitably leading to territorial loss and displacement.
There is a theory among scholars that suggests the tribe of Dan migrated northwards in search of better resources and security. Some believe that they left their assigned land and resettled in the areas near Mount Hermon and Paneas, modern-day Tel Dan. The archaeological evidence found at this location supports this theory, indicating a prosperous settlement by the Danites during this time.
However, there is another perspective that argues for a different path taken by the tribe of Dan. It is proposed that the Danites eventually left their assigned region and traveled westward, eventually settling in the land of the Philistines. This theory holds that they assimilated with the Philistine culture and lost their distinct Israelite identity.
The Book of Judges in the Hebrew Bible provides additional insights into what might have transpired with the tribe of Dan. In Judges 18, it is recounted that a group of Danite men sought new territory and spies were sent to explore a suitable location. They discovered the city of Laish and, impressed with its richness and peacefulness, decided to conquer it. The Israelite tribe of Dan managed to capture Laish and renamed it Dan after their ancestor. This event could explain the disappearance of Dan from their original territory.
Nonetheless, this account also opens up another possibility: that the tribe of Dan divided into separate groups. Some members may have chosen to remain in their assigned territory, while others migrated to Laish/Dan, or even set off to unknown destinations. Due to the scarcity of historical evidence and the complexities of ancient migrations, it is challenging to ascertain the exact fate of the tribe of Dan.
One theory suggests that the tribe of Dan may have assimilated into other Israelite tribes, losing their distinct identity. Since the tribes were constantly interacting and intermarrying, this theory posits that Danites might have been absorbed into neighboring tribes, assuming their customs and practices.
Another theory claims that the tribe of Dan faced continued external pressure and threats, eventually leading to their dispersion among other nations. The Assyrians and Babylonians, known for their conquests during the ancient world, may have played a role in scattering the Danites among different territories as they subjugated the region.
There is another interesting theory they may be in Greece. If your interested in it there is a video on YOU TUBE. It is 23 min.; https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iuqumwTKWUE&list=PLaJPl4kHzkvJh3PQ0yTGt2yaQXsVIfKNw&index=16
Overall, the fate of the Israelite tribe of Dan remains uncertain, clouded by both historical obscurity and different interpretations. Whether they migrated to new lands, assimilated into other tribes, or fell victim to foreign invasions, the exact sequence of events that led to the disappearance of Dan as a distinct tribe remains a mystery. However, with ongoing archaeological research and further analysis of ancient texts, we may gain a clearer understanding of what happened to this enigmatic tribe.